Wiring batteries in series vs parallel can feel like a life-or-death decision for your power system. Understanding the difference between them is essential if you have multiple batteries you want to connect together. Series configurations boost voltage, perfect for high-demand devices, while parallel setups enhance capacity, ensuring longer run-times. But what happens if one battery fails? Therefore, let's find out how to wire battery in series vs parallel and when to use them properly.
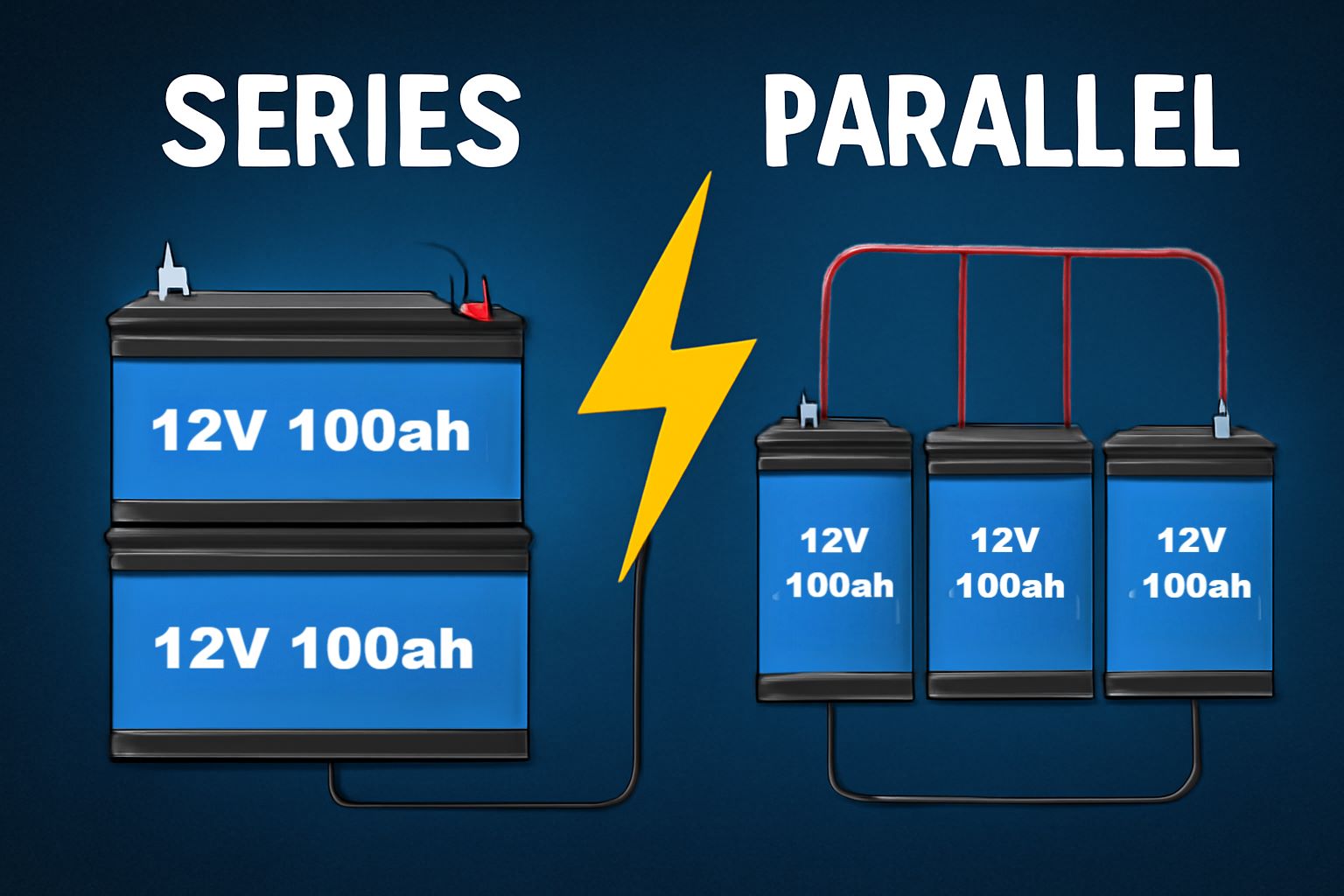
When deciding how to wire batteries, understanding the core differences between series and parallel configurations is essential for optimizing your power system.
Charging batteries in series vs parallel fundamentally affects voltage and current capacity. In series, you connect batteries positive to negative, increasing voltage while maintaining the same amp-hour rating. For example, if you have two 12V 100ah batteries, wiring them in series will yield 24V at 100 Ah capacity.
Conversely, when charging batteries in parallel, you connect all positive terminals together, which maintains voltage but sums the amp-hour capacity. This means two 12V 100ah batteries provide 12V at 200 Ah.
Each configuration has its advantages, influencing your system's efficiency and requirements.
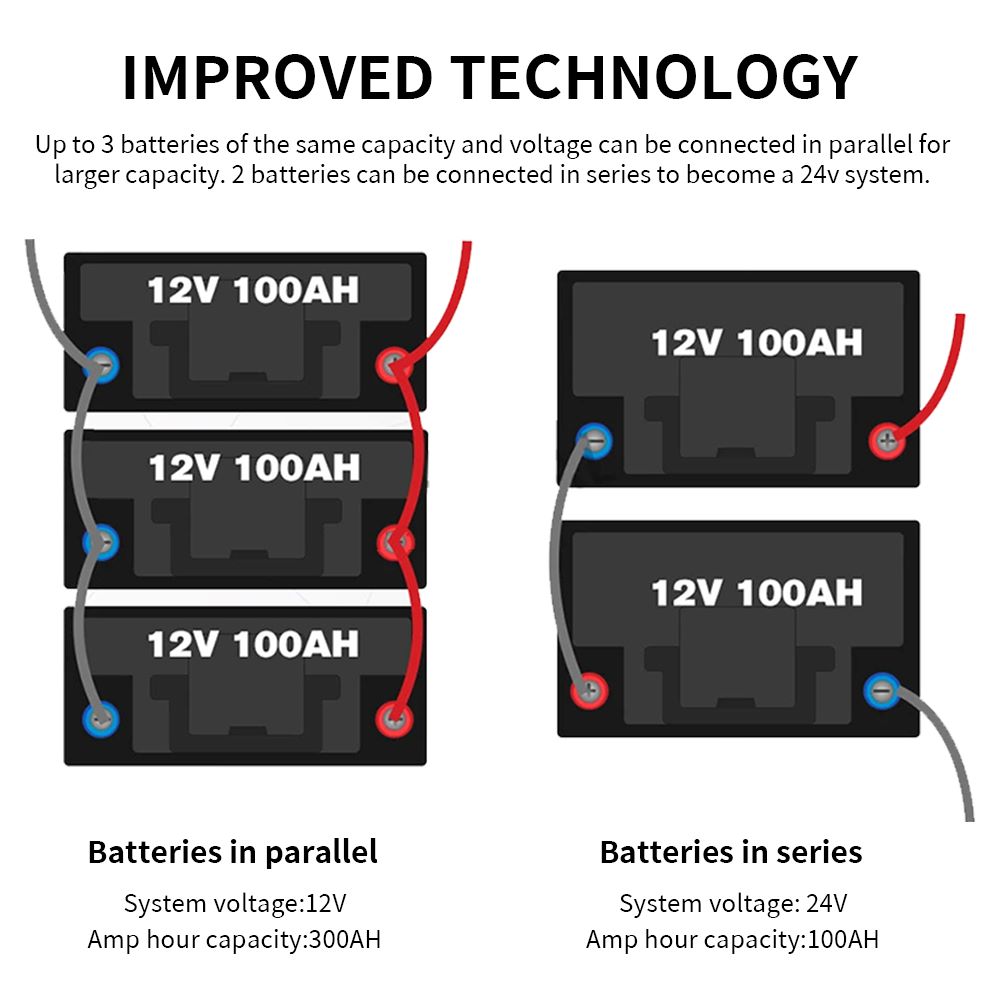
OK, and now, we will continue to know more about how to wire batteries. Wiring multiple batteries in series is a straightforward process that can greatly increase your system's voltage.
You'll connect the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of the next, ensuring compatibility in voltage and capacity.
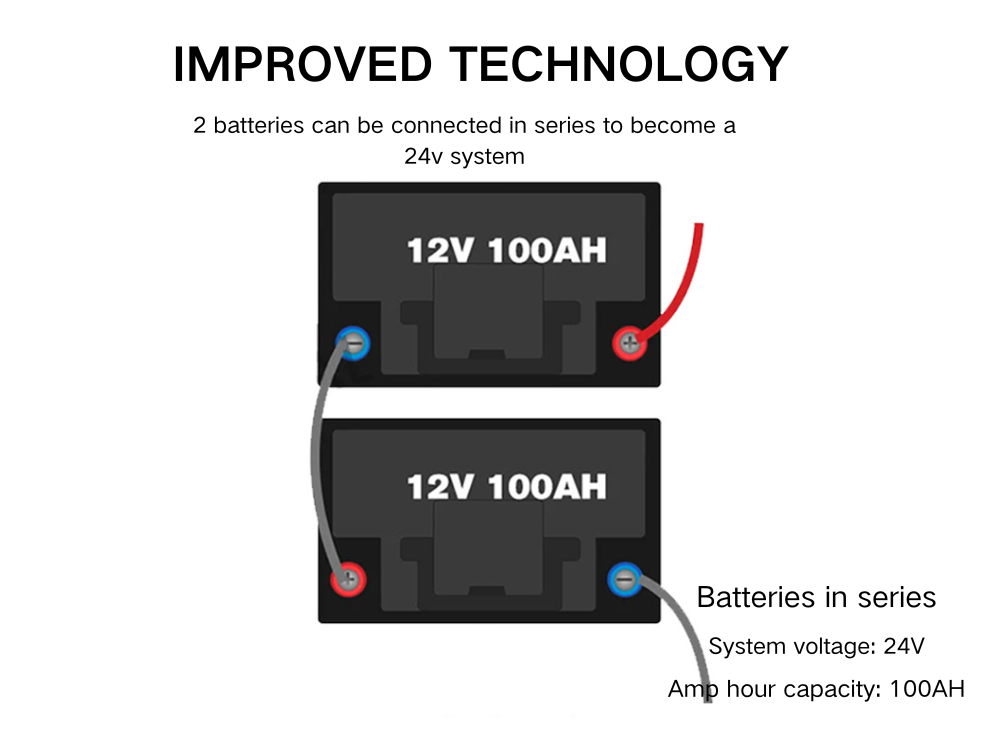
For example, in the next photo, two 12v 100ah batteries are wired in series. As you can see, the negative terminal on the first battery is connected to the positive terminal on the second. Thus, the system’s voltage will increase to 24 volts while the total capacity will remain at 100 Ah.
Connecting batteries in series offers several advantages, particularly when it comes to achieving higher voltage levels for various applications.
By wiring batteries in series, you can leverage the following benefits:
These advantages make series configurations particularly effective for larger power systems, ensuring peak performance while maintaining control over energy delivery. Thus, if you have multiple batteries in the same voltage and want to get high voltage outputs, wires batteries in series is a good choice for you.
While series configurations can effectively increase voltage, they come with notable disadvantages that you should consider. For example, in a battery system wired in series, if any single battery fails, the entire system loses power, which can lead to significant downtime. And then all equipment must also be compatible with the higher voltage, so that can be used safely.
Managing the health of each battery is essential, as imbalances can lead to reduced performance and lifespan for the entire series configuration.
To wire batteries in series effectively, start by verifying that all batteries are of the same voltage and capacity, as mismatched batteries can lead to performance issues.
Follow these steps for a precise setup:
The number of batteries you can connect in series depends on the voltage requirements of your application and the manufacturer’s specifications.
Each battery adds its voltage to the total output, but the amp-hour capacity remains unchanged. For instance, wiring two 12V batteries in series gives you 24V, and three yields 36V.
As a professional lifepo4 battery manufacturer, we will strictly inform our customers of the precautions regarding battery parallel or series connection. So that you must consider the limits set by the battery manufacturer; exceeding this can risk damage or failure. Always verify that the batteries have the same voltage and capacity ratings before connecting.
Proper management of battery health is essential to prevent system failure, especially since a single failing battery can compromise the entire series connection.
Related Article: https://gdleappower.com/can-you-charge-a-damaged-battery/
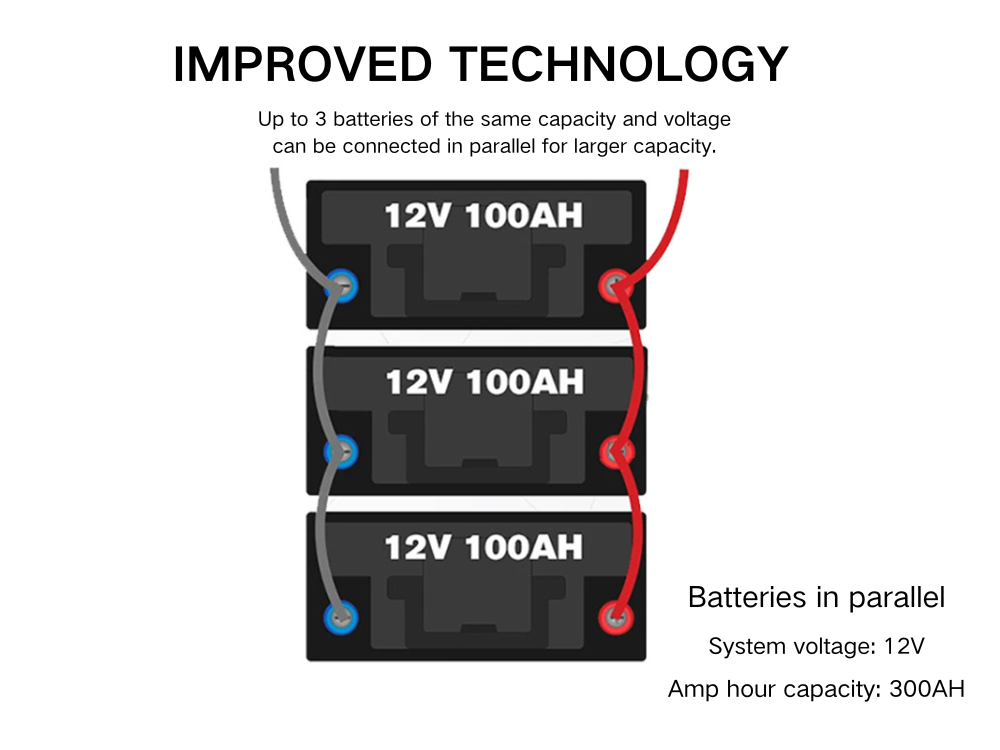
To wire multiple batteries in parallel, it is different from wiring in series. You'll need to connect all positive terminals together and all negative terminals together to achieve this configuration effectively.
For example, three 12v 100ah batteries are wired in parallel. The negative terminal on the first battery is connected to next negative terminal. And here it is totally different from batteries in series. the system’s voltage will remain 12 volts while the total capacity increase to 300 Ah.
Wiring batteries in parallel offers distinct advantages that can enhance your energy system's performance.
Here are three key benefits:
These advantages make parallel configurations particularly appealing for applications where extended power availability and system resilience are vital.
One significant issue to wire batteries in parallel is the increased current draw, which necessitates using thicker cables to prevent overheating and voltage drop. Additionally, longer charging times are common with larger parallel banks, potentially hindering performance during peak usage.
Therefore, while parallel wiring adds capacity, it introduces challenges that require meticulous management.
Connecting batteries in parallel effectively increases your system's amp-hour capacity without altering the voltage. To wire your batteries correctly, follow these steps:
How many batteries can you wire in parallel? There is no limit about the number of batteries you could connect. You can wire as many batteries as you need, provided they share the same voltage and capacity ratings.
Each parallel connection maintains the system voltage while increasing the overall amp-hour capacity. This configuration allows for redundancy; Even one battery fails, the others can continue functioning.
But remember, the more batteries you add in a parallel, the more long time for you to charge.

When considering to wire batteries in series and parallel together, it’s essential to understand the implications of each configuration and how to connect (the steps as we mentioned before). If you ask me about this question, my answer is Yes, you can.
You can indeed wire batteries in both series and parallel, which is series-parallel connected batteries.
Series-parallel connection allows for greater flexibility, enabling you to achieve desired voltage and capacity by creating series-parallel setups.
If you have any question with wiring batteries in series, parallel or series-parallel, please feel free to contact us.
Generally speaking, wiring lifepo4 batteries in series vs parallel don't give more power for using. Because as we mentioned before, series configurations boost voltage, perfect for high-demand devices, while parallel setups enhance capacity, ensuring longer run-times. However, if considering power output, when total energy remains consistent, series arrangements can be more efficient for high-load applications.
Therefore, no matter you charge batteries in series vs parallel, it will help you to boost voltage or enhance capacity instead of giving more power. I think you should know that clearly.
Choosing batteries in series vs parallel depends largely on your specific power requirements and application goals. Each configuration has distinct advantages
Ultimately, your choice hinges on balancing voltage, capacity, and efficiency for your specific application.
You shouldn't mix different battery types in configurations. Doing so can lead to imbalances, reduced efficiency, and potential damage. Always match voltage and capacity ratings to guarantee peak performance and longevity of your battery system.
Temperature greatly impacts battery performance. For example, in cold weather, a lithium battery's capacity can drop by 20%. You need to monitor temperatures closely to maintain ideal performance and prevent premature failure in any configuration.
When wiring batteries, you must guarantee proper connections, use appropriate fuses, and maintain uniform battery types. Always monitor voltage levels and avoid overcharging to prevent thermal runaway and potential failures within the system.
When it comes to battery lifespan, you need to take into account factors like charging cycles and temperature. In series, a single failure affects the whole system, while parallel setups allow others to continue functioning, enhancing overall longevity.
Battery management systems actively monitor and control charging methods, ensuring ideal voltage and current delivery. They protect against overcharging and balancing, enhancing efficiency and lifespan by maintaining healthy battery conditions, regardless of series or parallel configurations.
In the world of battery charging, choosing batteries in series vs parallel configurations is like maneuvering through a maze of voltage and capacity. Picture your device: will it thrive on the high voltage of series or the extended runtime of parallel? Each path has its risks and rewards. By carefully weighing your application’s needs, you can illuminate the best choice for your setup. Ultimately, it’s not just about power; it’s about crafting a reliable energy solution tailored to your demands.

"We strive to deliver real value for our customers through distinctive design, superb quality and excellent customer service at prices that reflect the real worth of our products."
---Emmy Zheng, Author



